Design Computing Studio 3 - Proposal
Projects
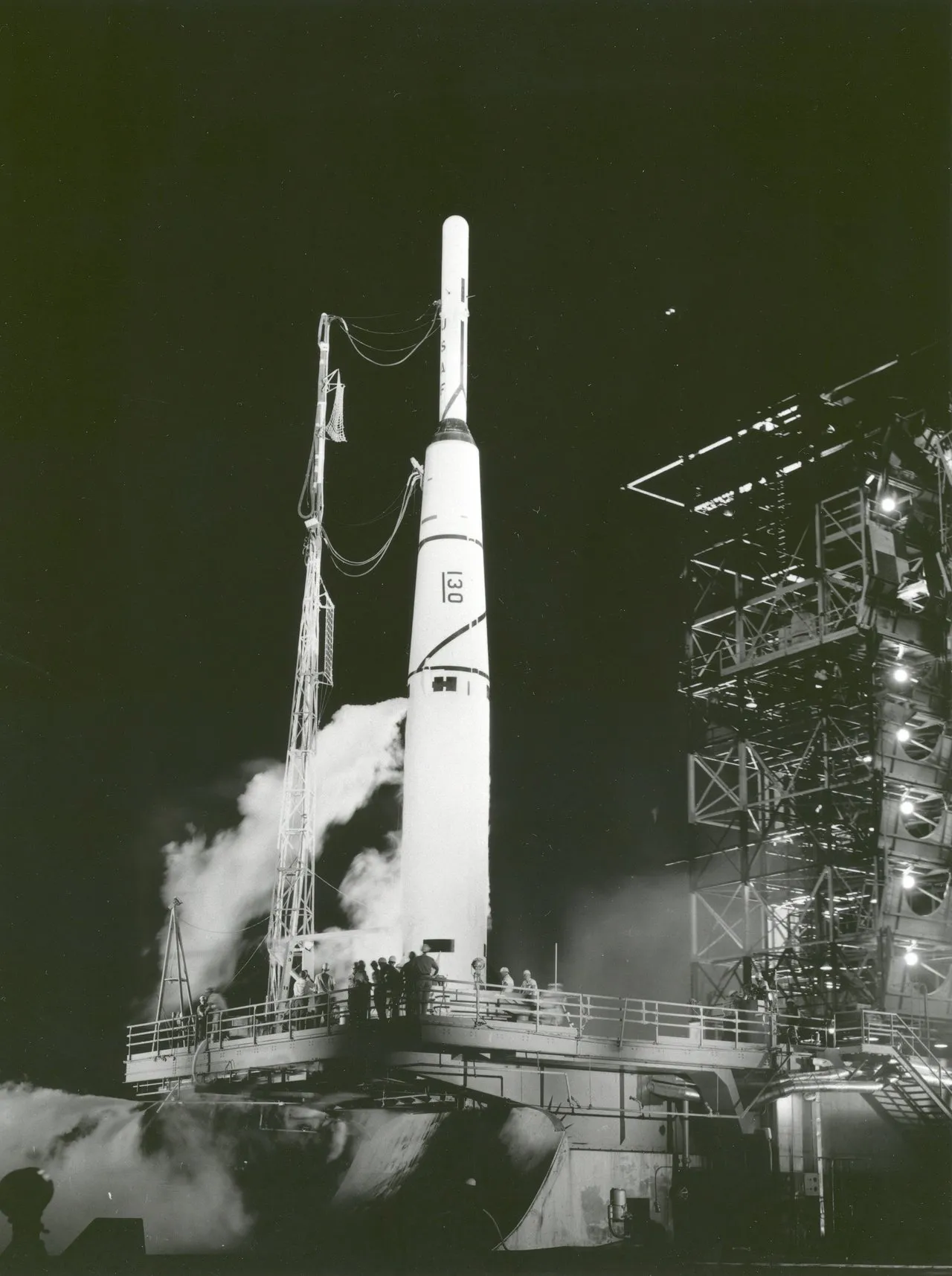

Able 2 (Pioneer 1)
Able 2, later named Pioneer 1, was the first spacecraft launched by NASA. Due to a malfunction, the spacecraft never reached the Moon but did return data on the near-Earth environment.

3D Tissue Chips
Small devices about the size of a USB drive, 3D tissue chips replicate cells of specific organs – heart, pancreas, liver, and others.

Advanced Plant Habitat
The Advanced Plant Habitat is the largest, fully automated plant growth research facility used to conduct plant bioscience research on the International Space Station (ISS).
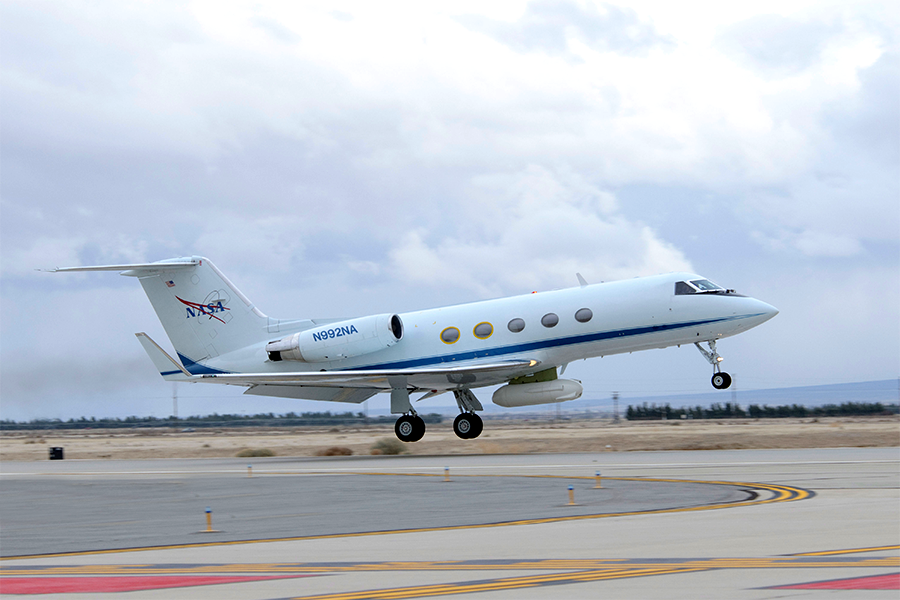

AirMOSS
AirMOSS measured soil moisture of plant roots to help determine the amount of carbon being exchanged between plants and the atmosphere.
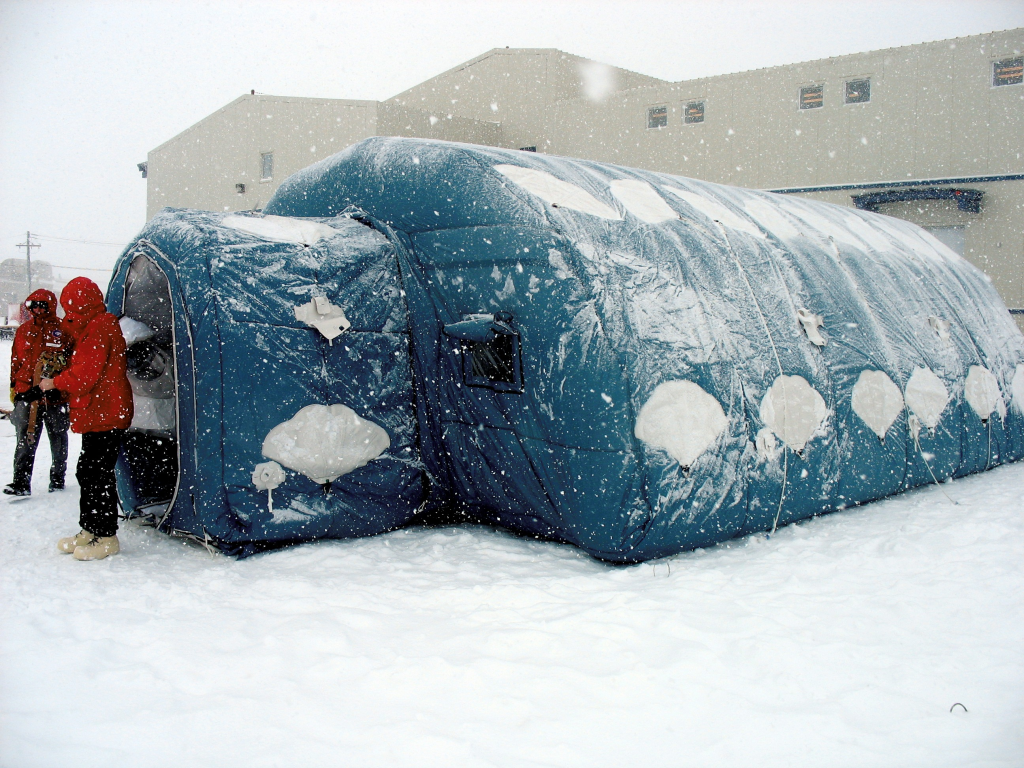

Antarctic Stations
Antarctica’s climate, terrain, temperature, and isolation provide an environment on Earth that closely parallels the conditions of isolation and stress that astronauts will face on long-duration missions in space.
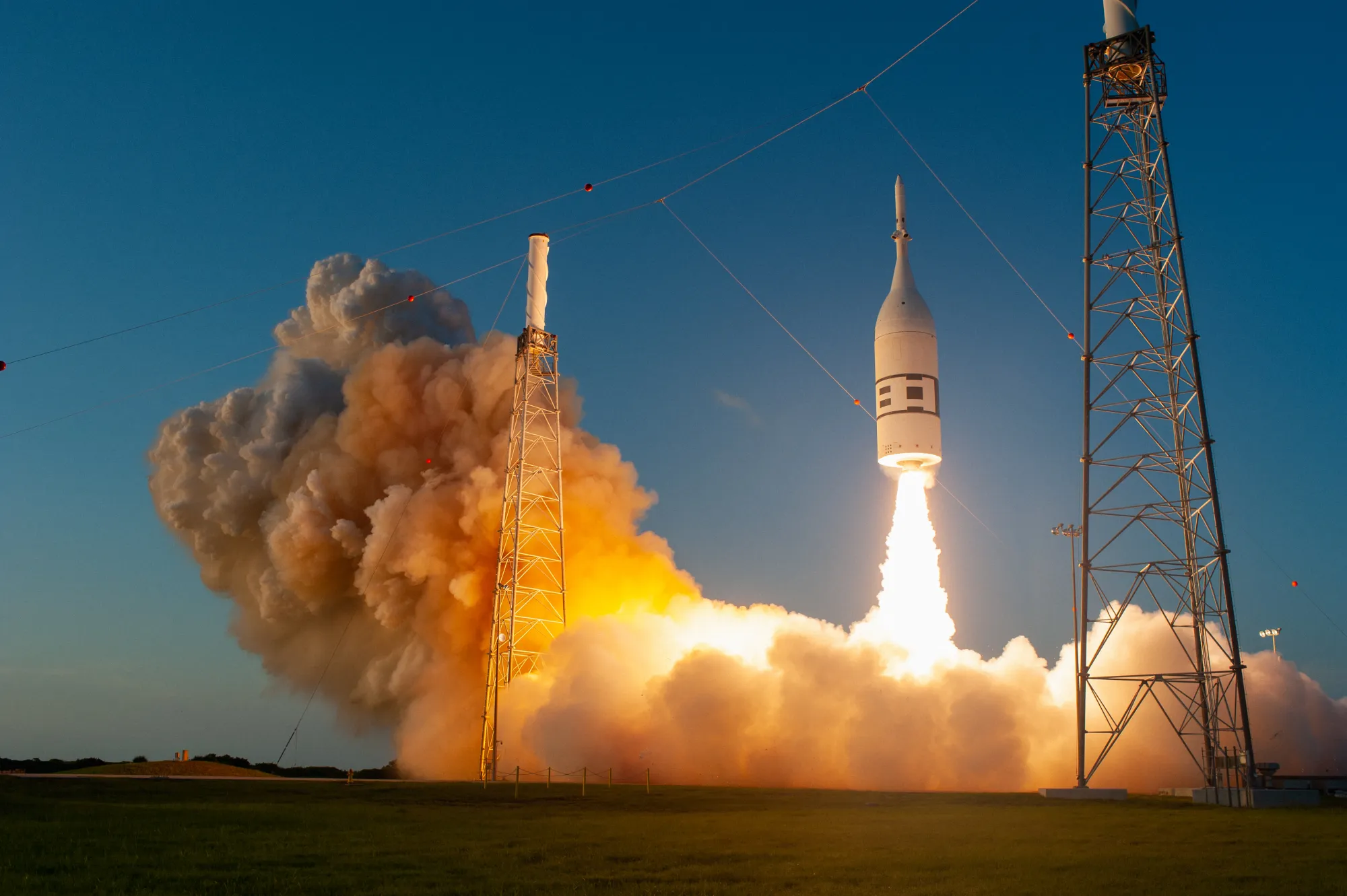

Ascent Abort-2
On July 2, 2019, NASA conducted a successful test known as Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2), which tested the Orion launch abort system (LAS), a critical safety system that sits atop Orion at launch and during ascent.
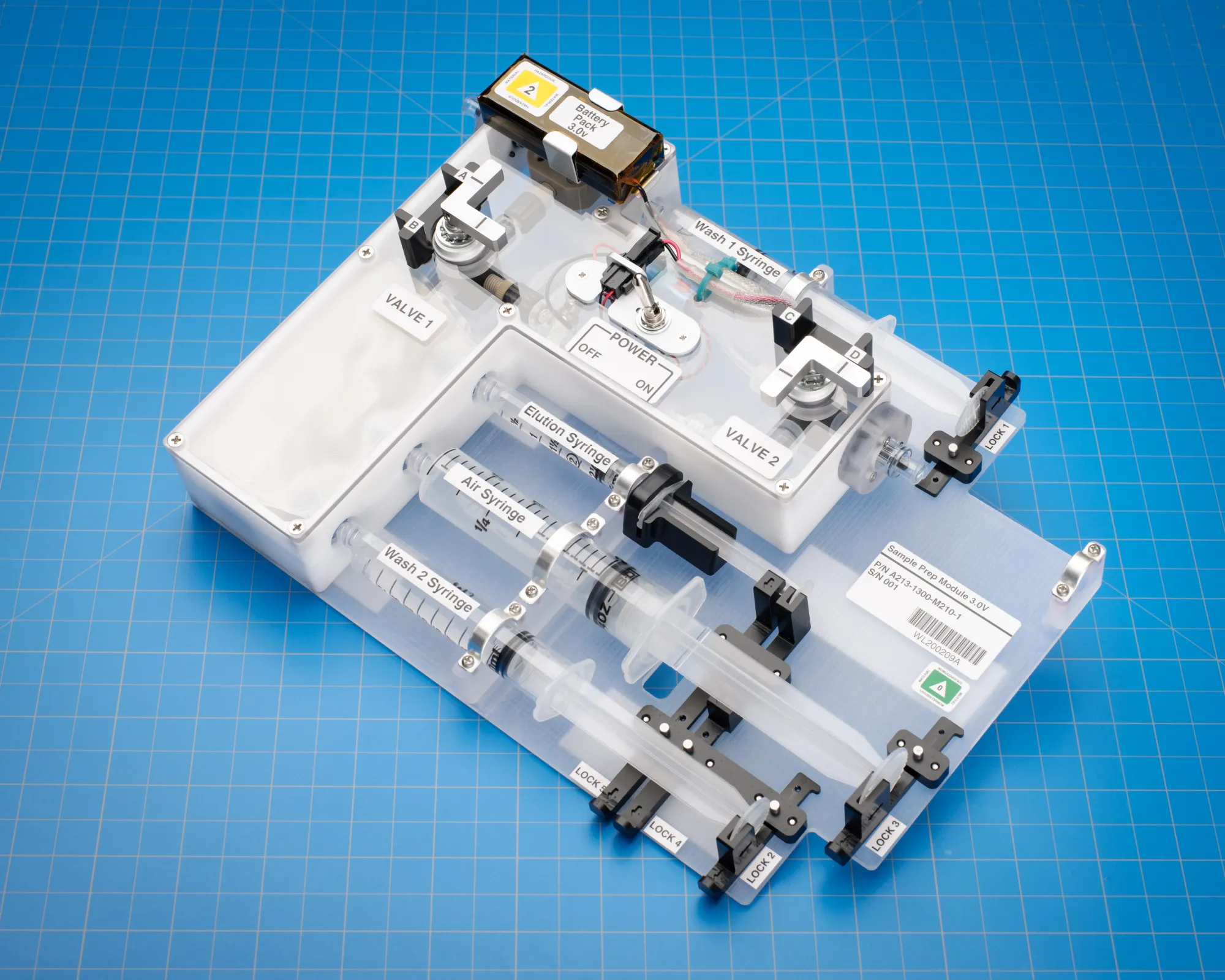
WetLab-2
WetLab-2 is a research platform for conducting real-time gene analysis aboard the International Space Station (ISS).
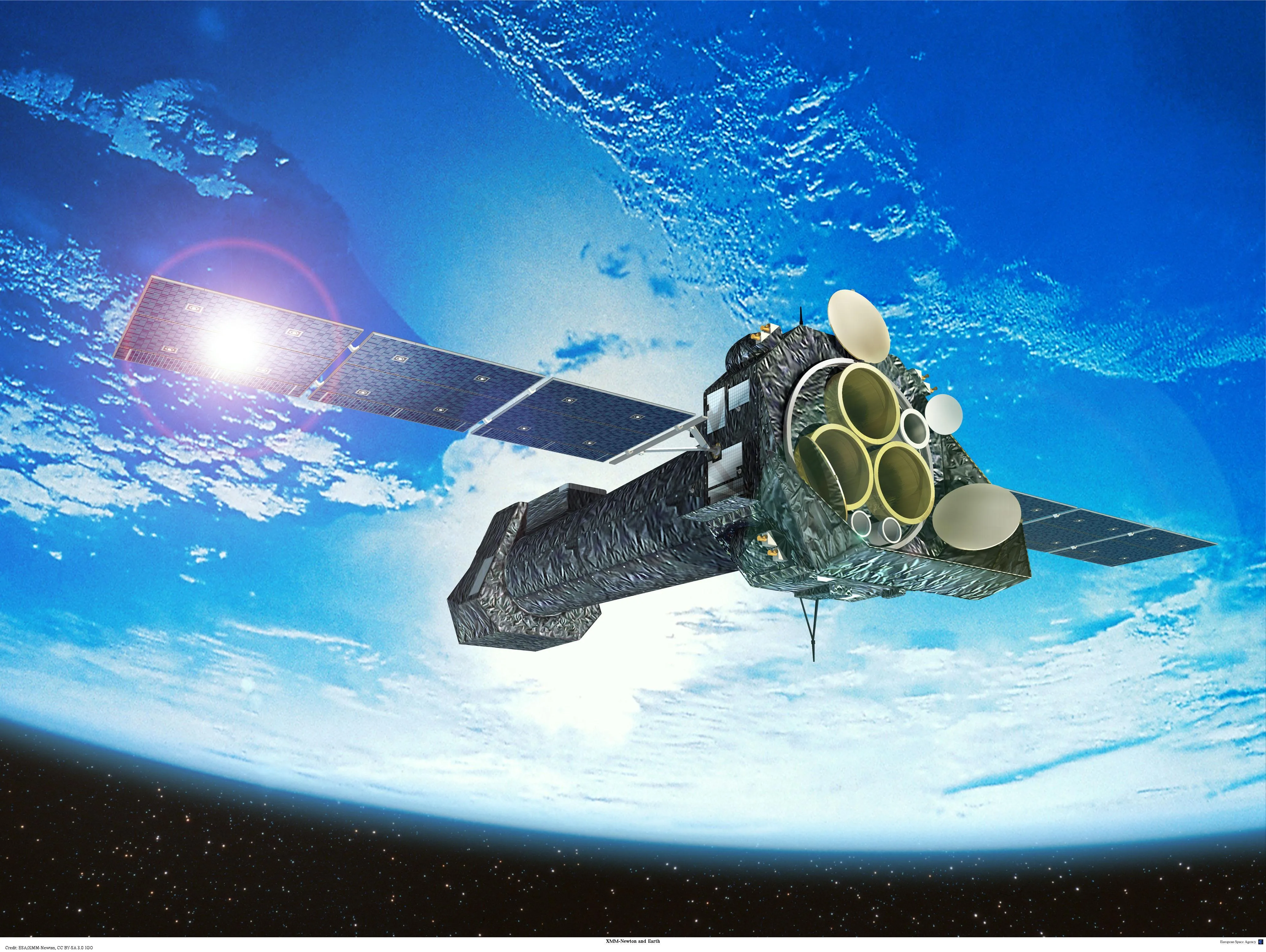

XMM-Newton
ESA's (European Space Agency) XMM-Newton is a space observatory whose X-ray and optical/ultraviolet telescopes study a wide variety of objects, from distant galaxy clusters to solar system planets.